
There are many aspects to consider in implementing enterprise risk management. These include the organization's culture, the processes and methodologies that will be used and the organizational structure. These are the essential steps. First, identify the risks and opportunities that can be posed to you. Next, develop probability distributions that can be used to assess and quantify the risks. Finally, integrate the risks and their impacts to key performance metrics. Once you have identified and quantified the risks, you can create a plan for reducing them.
Organizational culture
Organizational culture is crucial for the success of risk-management. Its objectives must be aligned with its mission, values, and strategy. This culture must be transparent and dynamic. It should encourage proactive feedback and provide uniform responses to risks. You should monitor its impact on employees' decisions. Decisions that go against the policies or risk profile are a sign of a weak culture and low competitive strength.
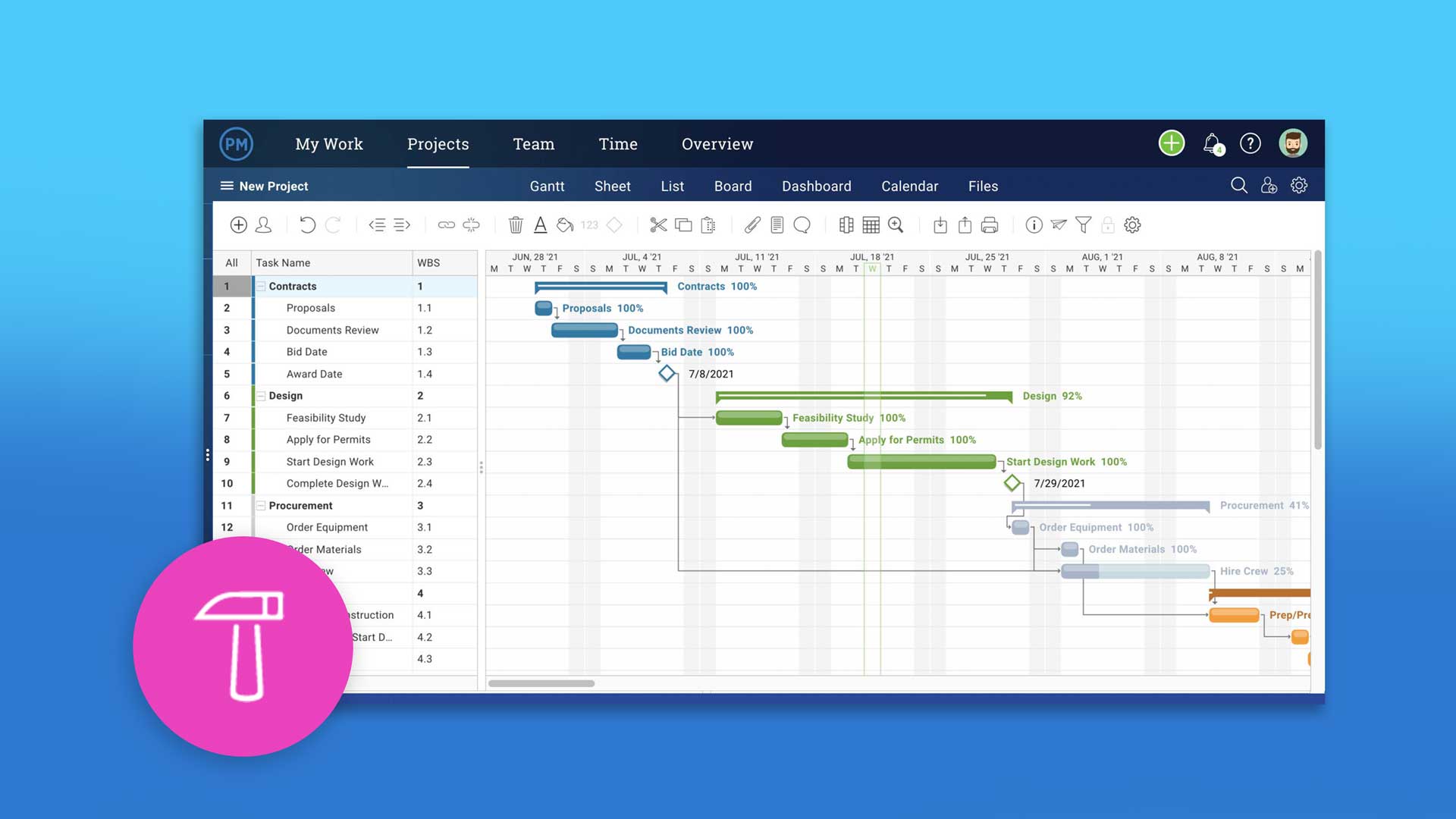
Processes
The first step to creating an effective and robust risk management program is to develop processes. To measure and categorize risk, you should use a matrix or risk register. A description, a cause and consequences as well as a mitigation plan should be included in the risk register. The risk register should also identify the responsible party. It is important that the risk register be as specific as possible to avoid misunderstandings, as this will help the organization avoid mistakes.
Methods
Implementing enterprise risk management (ERM) is an important step in the governance of a business. This process helps in evaluating, implementing and reporting on various types of risks. These measures can be used to assist companies in managing their risk, preventing surprises, and improving performance and growth. ERM helps to set worthy business objectives. ERM can be used to monitor external and internal risk. As the business shifts to cloud-based services, this type of management becomes more important.
Organizational structure
Enterprise risk management can only be successful if the leaders of the organization have a common culture of compliance. In addition, leaders should make sure that their companies' controls are effective, consider all relevant risks, and encourage an escalation process. Leaders should encourage open discussion and information sharing to ensure that effective risk management is achieved. They also need to be accountable for their actions. Senior management and the board of directors are responsible for setting the tone and guiding an organization's compliance culture and risk culture.
Functions
A board of directors may have a high-level discussion about enterprise risk management. These functions encourage managements to look at all aspects of risk. These functions are essential for ensuring smooth operation of a business. These functions may also be useful for improving the culture of an organisation. Here are some of the functions of enterprise risk management. - All risks are evaluated and managed by the management. - Risk will be taken into account in the organisation's strategy planning process.

Stakeholders
The stakeholder analysis is a fundamental part of the project management process. It assists project managers in determining which stakeholder is most influential and their role in the project. Stakeholder analysis helps project managers to identify the risks and possible consequences on each stakeholder. They can also organize the stakeholders based on their contribution to the project's success. These are the four steps you should follow to conduct stakeholder analyses.
FAQ
How does Six Sigma work
Six Sigma uses statistical analysis for problems to be found, measured, analyzed root causes, corrected, and learned from.
The first step in solving a problem is to identify it.
The next step is to collect data and analyze it in order to identify trends or patterns.
Next, corrective steps are taken to fix the problem.
Finally, data will be reanalyzed to determine if there is an issue.
This continues until you solve the problem.
What role should a manager play within a company
The role of a manager varies from one industry to another.
A manager is generally responsible for overseeing the day to day operations of a company.
He/she makes sure that the company meets its financial obligations, and that it produces goods or services that customers desire.
He/she ensures that employees follow the rules and regulations and adhere to quality standards.
He/she designs new products or services and manages marketing campaigns.
What does it mean to say "project management"
That is the management of all activities associated with a project.
We help you define the scope of your project, identify the requirements, prepare the budget, organize the team, plan the work, monitor progress and evaluate the results before closing down the project.
Statistics
- The profession is expected to grow 7% by 2028, a bit faster than the national average. (wgu.edu)
- UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers on its site. (upcounsel.com)
- Your choice in Step 5 may very likely be the same or similar to the alternative you placed at the top of your list at the end of Step 4. (umassd.edu)
- As of 2020, personal bankers or tellers make an average of $32,620 per year, according to the BLS. (wgu.edu)
- Our program is 100% engineered for your success. (online.uc.edu)
External Links
How To
How can you implement Quality Management Plan (QMP).
Quality Management Plan (QMP), which was introduced in ISO 9001:2008, provides a systematic approach to improving processes, products, and services through continual improvement. It focuses on the ability to measure, analyze and control processes and customer satisfaction.
QMP is a common method to ensure business performance. QMP improves production, service delivery, as well as customer relations. QMPs should address all three dimensions: Products, Services, and processes. If the QMP only covers one aspect, it's called a "Process QMP". The QMP that focuses on a Product/Service is called a "Product." QMP. The QMP that focuses on customer relationships is known as the "Customer" QMP.
When implementing a QMP, there are two main elements: Scope and Strategy. These elements can be defined as follows.
Scope is what the QMP covers and how long it will last. This scope can be used to determine activities for the first six-months of implementation of a QMP in your company.
Strategy: This describes the steps taken to achieve the goals set out in the scope.
A typical QMP includes five phases: Design, Planning, Development and Implementation. Each phase is described below:
Planning: This stage determines the QMP goals and prioritizes them. To understand the expectations and requirements of all stakeholders, the project is consulted. Next, you will need to identify the objectives and priorities. The strategy for achieving them is developed.
Design: The design stage involves the development of vision, mission strategies, tactics, and strategies that will allow for successful implementation. These strategies are implemented by the development of detailed plans and procedures.
Development: Here, the team develops the resources and capabilities that will support the successful implementation.
Implementation: This is the actual implementation and use of the QMP's planned strategies.
Maintenance: It is an ongoing process that maintains the QMP over time.
The QMP must also include several other items:
Stakeholder Involvement: Stakeholders are important for the success of the QMP. They should be involved in planning, design, development and implementation of the QMP.
Initiation of a Project: A clear understanding and application of the problem statement is crucial for initiating a project. In other words, they must understand the motivation for initiating the project and the expectations of the outcome.
Time frame: The QMP's timeframe is critical. A simple version is fine if you only plan to use the QMP for a brief period. You may need to upgrade if you plan on implementing the QMP for a long time.
Cost Estimation - Cost estimation is an important part of the QMP. It is impossible to plan without knowing what you will spend. Therefore, cost estimation is essential before starting the QMP.
QMPs are not only a document, but also a living document. This is the most important aspect of QMPs. It evolves as the company grows and changes. It should be reviewed regularly to ensure that it meets current needs.