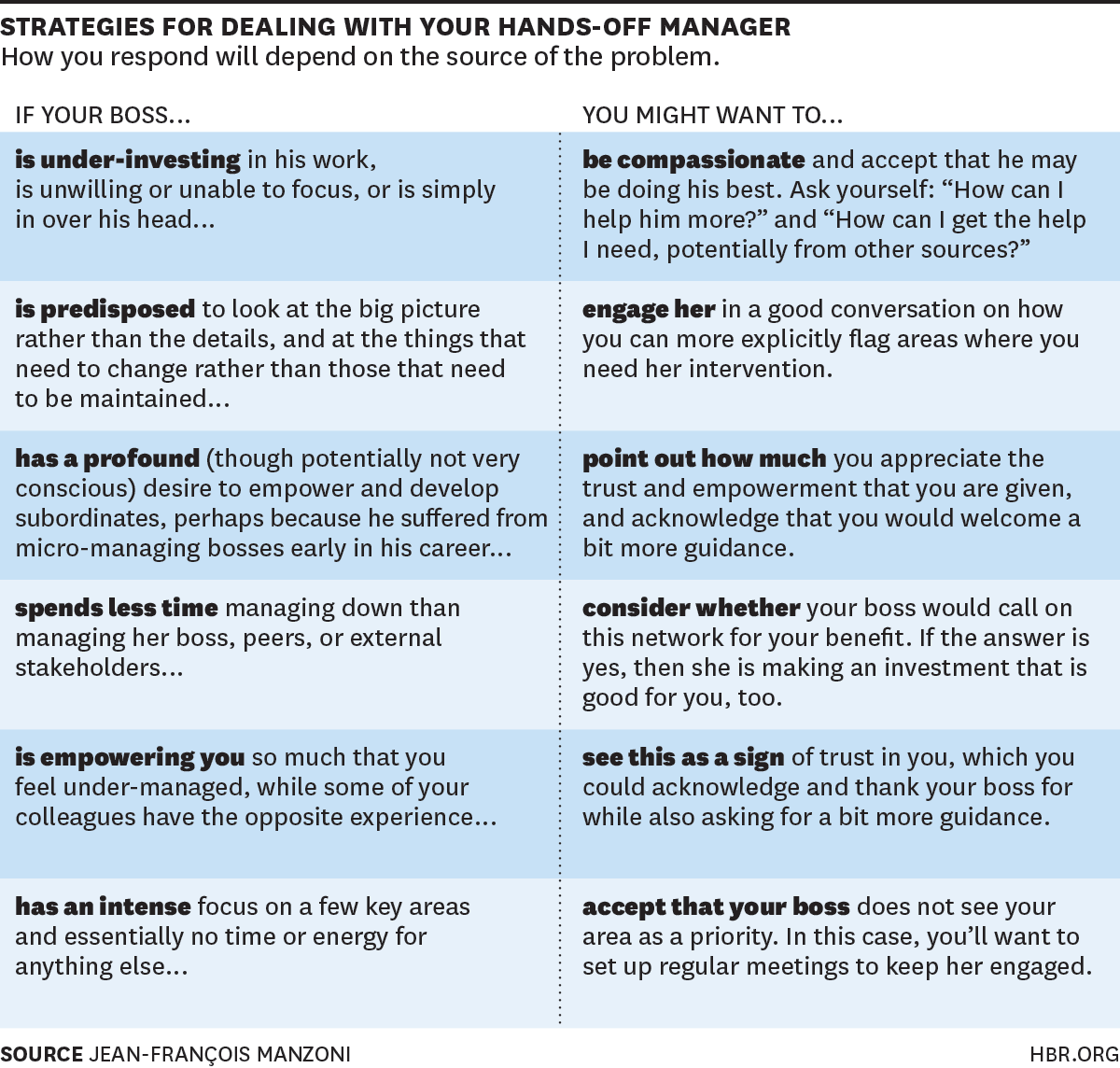
While it can be difficult to accept safety as part of a culture, it can be possible. We'll be talking about how to establish a culture of safety in this article. The steps in this process will vary depending on your organization. The first step in creating a safe environment is to make everyone feel comfortable. Focus groups is a common way to accomplish this. Focus groups allow you to ask employees and stakeholders for feedback. This will help to create a culture that is well-designed.
Accepting safety as part of your culture
Safety as a culture involves focusing on the behavior of employees and acknowledging that safety must be shared. This requires extensive training and education. It is a process that requires support from all levels. It is important to embrace safety as a part of a company's culture. How can you do that? How can you create an environment where safety is valued? Here are some tips:
Culture shifts are the key to solving workplace safety issues. The solution to workplace safety problems lies in a culture shift. People will start to own the process by changing their perceptions of safety. Safety as a culture can empower employees to be safety leaders. Safety management systems need to train employees on how to lead and coach others. In addition, employees must have a genuine commitment to safety.
Safety culture at the analytical stage
An effective safety culture is one that encourages employees to report potential safety hazards. Trust is crucial for this. Employees should feel confident that they won't lose their job or be punished for reporting problems. All information must be kept confidential by senior management. Employees need to feel confident that their information will always be dealt with promptly.
Safety culture begins with the recognition of problems, analysis and reporting of the results. These processes include corrective measures and root cause analysis. These tools allow you to determine the root causes of injuries and provide safe care. This stage is critical for creating safety culture. It is also important to identify the values and attitudes that drive the safety culture.
Focus groups can be used to help create a safety culture
Creating a safety culture requires a strategic roadmap and flexibility. Employees must feel comfortable sharing concerns and ideas regarding workplace safety. To facilitate this, employees should feel comfortable sharing their concerns anonymously through a whistleblowing process. Instead of punishing people for pointing out problems, emphasize positive reinforcement. Positive reinforcement increases trust, morale, and employee engagement. Creating a safety culture is a long-term process, and the benefits will be worth it.
To create a positive safety culture, companies must first identify limiting mindsets. Once they have identified the mindsets, they need to change their mind-set. In other words, they must build trust among employees and create a positive environment that will encourage them to report incidents and near misses. This will encourage employees to report incidents and near misses as a reward. This will result in safer behavior.
FAQ
What are the four major functions of Management?
Management is responsible for planning, organizing, directing, and controlling people and resources. It includes the development of policies and procedures as well as setting goals.
Management is the ability to direct, coordinate, control, motivate, supervise, train, and evaluate an organization's efforts towards achieving its goals.
These are the four major functions of management:
Planning - Planning involves determining what needs to be done.
Organizing – Organizing means deciding how to organize things.
Directing - Directing means getting people to follow instructions.
Controlling: Controlling refers to making sure that people do what they are supposed to.
What is Six Sigma, exactly?
It is a way to improve quality that places emphasis on customer service and continuous learning. The goal is to eradicate defects through statistical techniques.
Motorola's 1986 efforts to improve manufacturing process efficiency led to the creation of Six Sigma.
The idea spread quickly throughout the industry, and today, many organizations are using six sigma methods to improve product design, production, delivery, and customer service.
What are the key management skills?
No matter if they are running a local business or an international one, management skills are vital. These skills include the ability manage people, finances and resources as well as other factors.
When you need to manage people, set goals, lead teams, motivate them, solve problems, develop policies and procedures and manage change, management skills are essential.
As you can see, there's no end to the list of managerial duties!
What role should a manager play within a company
Different industries have different roles for managers.
A manager generally manages the day to-day operations in a company.
He/she ensures that the company meets its financial obligations and produces goods or services that customers want.
He/she is responsible for ensuring that employees comply with all regulations and follow quality standards.
He/she plans and oversees marketing campaigns.
Six Sigma is so beloved.
Six Sigma can be implemented quickly and produce impressive results. It also provides a framework for measuring improvements and helps companies focus on what matters most.
Statistics
- The average salary for financial advisors in 2021 is around $60,000 per year, with the top 10% of the profession making more than $111,000 per year. (wgu.edu)
- UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers on its site. (upcounsel.com)
- This field is expected to grow about 7% by 2028, a bit faster than the national average for job growth. (wgu.edu)
- 100% of the courses are offered online, and no campus visits are required — a big time-saver for you. (online.uc.edu)
- As of 2020, personal bankers or tellers make an average of $32,620 per year, according to the BLS. (wgu.edu)
External Links
How To
How can you implement Quality Management Plan (QMP).
QMP (Quality Management Plan), introduced in ISO 9001,2008, provides a systematic method for improving processes, products, or services through continuous improvement. It emphasizes on how to continuously measure, analyze, control, and improve processes, product/service, and customer satisfaction.
The QMP is a standard method used to ensure good business performance. QMP improves production, service delivery, as well as customer relations. A QMP should include all three aspects - Processes, Products, and Services. A "Process" QMP is one that only includes one aspect. When the QMP focuses on a Product/Service, it is known as a "Product" QMP. QMP is also used to refer to QMPs that focus on customer relations.
Scope, Strategy and the Implementation of a QMP are the two major elements. These elements are as follows:
Scope: This determines the scope and duration of the QMP. For example, if you want to implement a QMP that lasts six months, then this scope will outline the activities done during the first six.
Strategy: This is the description of the steps taken to achieve goals.
A typical QMP consists of 5 phases: Planning, Design, Development, Implementation, and Maintenance. Below is a description of each phase:
Planning: In this stage the QMP's objectives and priorities are established. Every stakeholder involved in the project is consulted to determine their expectations and needs. After identifying the objectives, priorities, and stakeholder involvement, the next step is to develop the strategy for achieving these objectives.
Design: This stage involves the creation of the vision, mission, strategies and tactics necessary to implement the QMP successfully. These strategies are executed by creating detailed plans.
Development: Here, the team develops the resources and capabilities that will support the successful implementation.
Implementation: This is the actual implementation and use of the QMP's planned strategies.
Maintenance: Maintaining the QMP over time is an ongoing effort.
Additional items must be included in QMP.
Stakeholder involvement is important for the QMP's success. They should be involved in planning, design, development and implementation of the QMP.
Project Initiation: The initiation of any project requires a clear understanding of the problem statement and the solution. Also, the initiator should understand why they are doing it and what they expect.
Time Frame: It is important to consider the QMP's time frame. You can use a simplified version if you are only going to be using the QMP for short periods. You may need to upgrade if you plan on implementing the QMP for a long time.
Cost Estimation - Cost estimation is an important part of the QMP. It is impossible to plan without knowing what you will spend. The QMP should be cost-estimated before it can begin.
QMPs are not only a document, but also a living document. This is the most important aspect of QMPs. It evolves as the company grows and changes. It is important to review it periodically to ensure it meets all current requirements.